Art by PlaythinkAbstract
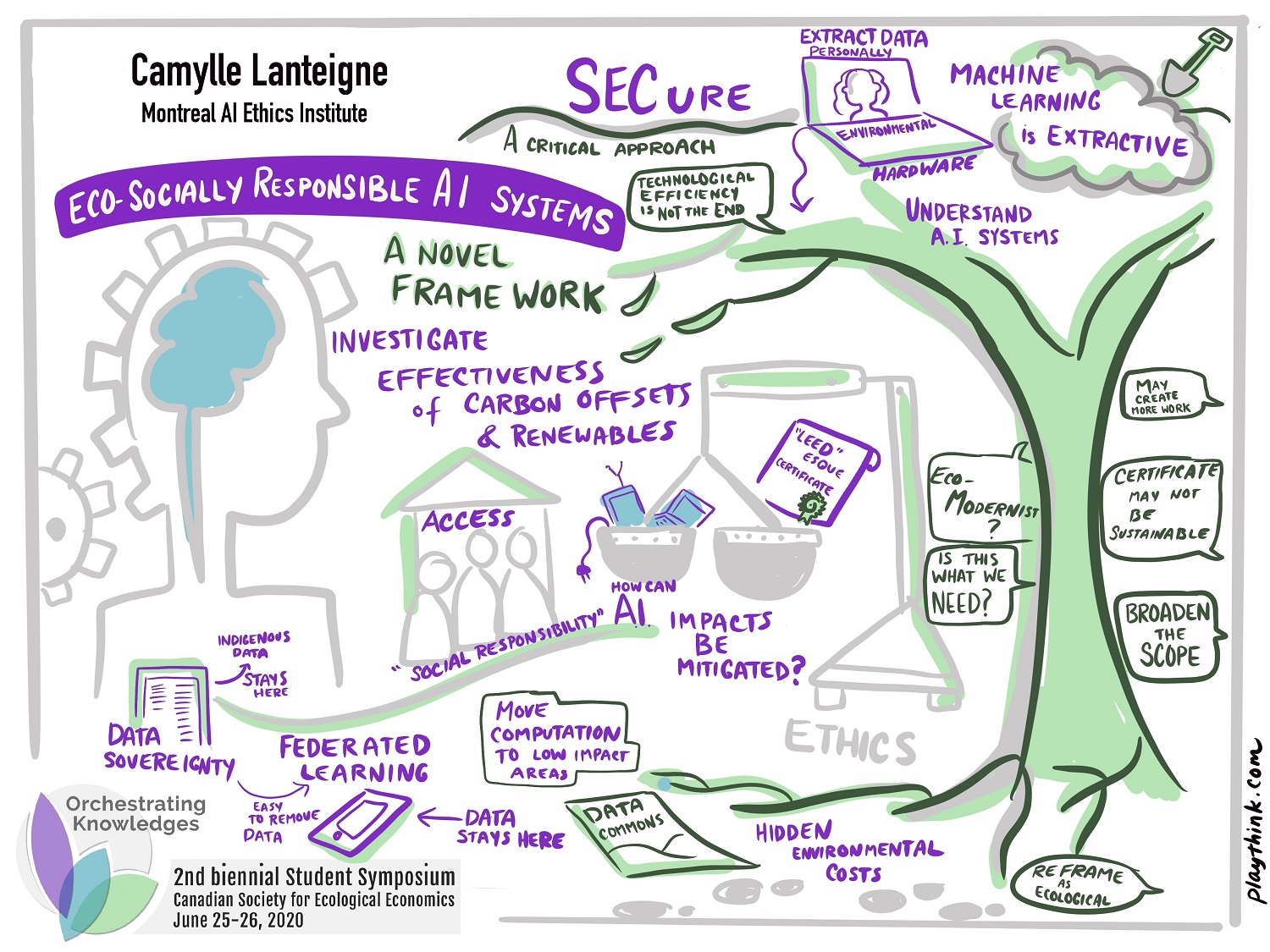
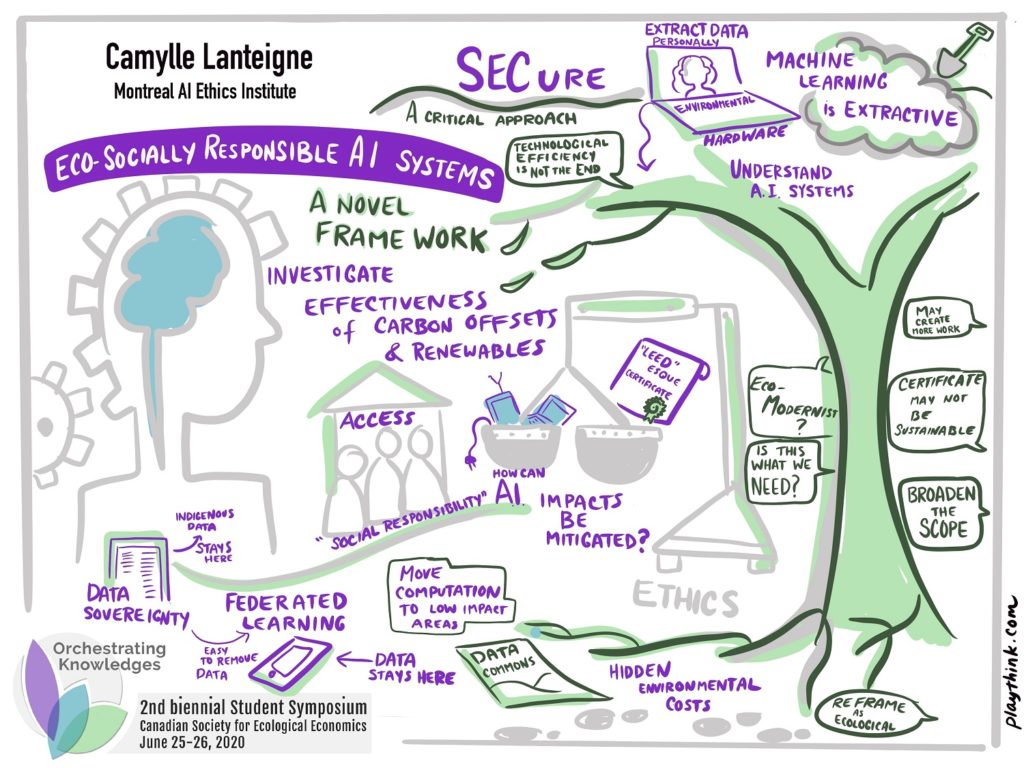
In a world increasingly dominated by AI applications, an understudied aspect is the carbon and social footprint of these power-hungry algorithms that require copious computation and a trove of data for training and prediction. While profitable in the short-term, these practices are unsustainable and socially extractive from both a data-use and energy-use perspective. This work proposes an ESG-inspired framework combining socio-technical measures to build eco-socially responsible AI systems. The framework has four pillars: compute-efficient machine learning, federated learning, data sovereignty, and a LEEDesque certificate.
Compute-efficient machine learning is the use of compressed network architectures that show marginal decreases in accuracy. Federated learning augments the first pillar’s impact through the use of techniques that distribute computational loads across idle capacity on devices. This is paired with the third pillar of data sovereignty to ensure the privacy of user data via techniques like use-based privacy and differential privacy. The final pillar ties all these factors together and certifies products and services in a standardized manner on their environmental and social
impacts, allowing consumers to align their purchase with their values.
