
🔬 Research Summary by Mohi Reza, a Computer Science Ph.D. Candidate at the University of Toronto and an Adaptive Experimentation Accelerator team member who won the Grand Prize in the $1M XPRIZE Digital Learning Challenge specializes in enhancing digital learning using field experiments powered by HCI, ML, and AI.
[Original paper by Mohi Reza, Nathan Laundry, Ilya Musabirov, Peter Dushniku, Zhi Yuan “Michael” Yu, Kashish Mittal, Tovi Grossman, Michael Liut, Anastasia Kuzminykh, and Joseph Jay Williams]
Overview: State-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) potentially transform our text composition and editing approach. However, the prevalent chat-based interfaces for LLMs often complicate the management of multiple text variations, leading to increased workload and interruption of the writer’s creative process. This paper introduces ABScribe, a novel interface designed to facilitate a rapid yet visually structured exploration of writing variations in human-AI writing tasks while minimizing task workload and preserving writers’ flow.
Introduction
“The only kind of writing is rewriting”
Ernest Hemingway, A Moveable Feast
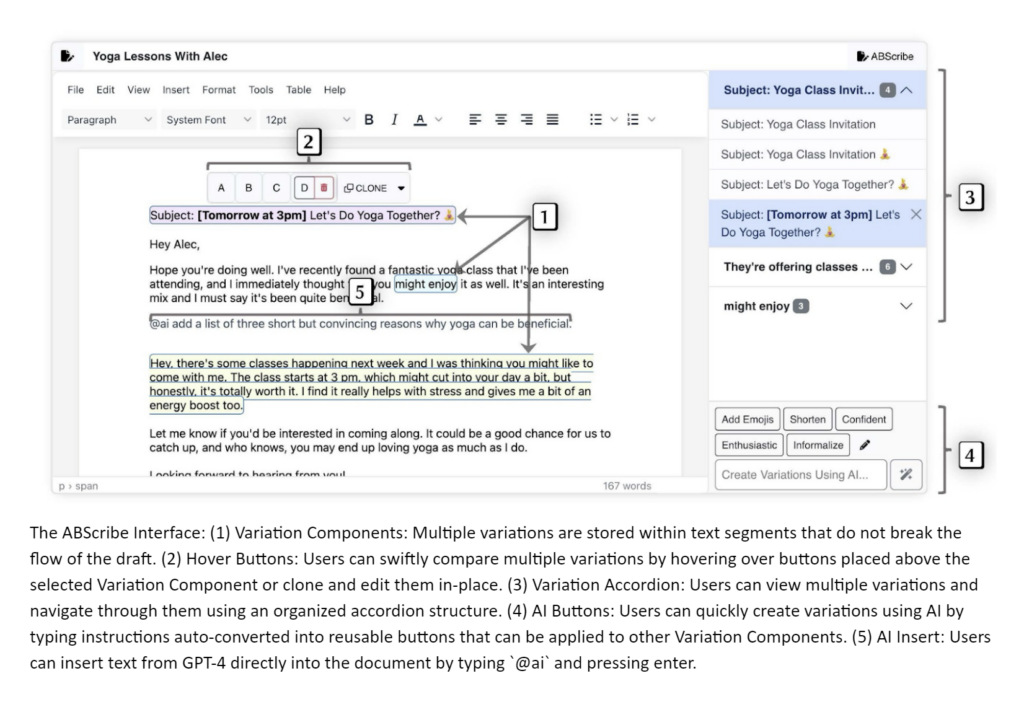
In the age of Generative AI, as tools like ChatGPT become our writing companions, revising text with AI assistance becomes a battle against the clutter of lengthy, unwieldy chat logs. This research investigates ways to improve a fundamental aspect of writing with AI: the iterative, granular, and non-linear revision process. It presents ABScribe, a novel Human-AI co-writing interface that eliminates the predominant chat-based UI of generative AI, enabling writers to manage multiple text variations effectively. ABScribe’s design enables the rapid generation and comparison of variations through an ensemble of novel interface elements, sidestepping the usual pitfalls of AI co-writing, such as excessive scrolling and cognitive overload. In a study with 12 writers, ABScribe significantly reduced the subjective task workload and improved users’ perceptions of the revision process. Interfaces like ABScribe can help us harness the full potential of AI in writing, transforming an explosion of ideas into a fountain of well-organized creativity.
Key Insights
Unlocking Creativity with AI
Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and traditional design practice encourage the parallel exploration of multiple variations to help avoid fixating on a single idea and to reduce the chances of eliminating rough but innovative ideas too early. Our research extends this principle to writing, proposing that AI can facilitate this exploration. However, the challenge lies in designing interfaces that prevent users from drowning in a sea of AI-generated content.
Moving beyond Chatbots
To ground our interface design, we distinguish between two kinds of Human-AI Co-Writing interfaces: the conversational interfaces, exemplified by ChatGPT, which mimic human dialogue but may hinder the management of multiple text variations due to their linear structure, and the ‘In-Place’ interfaces, which seamlessly blend AI suggestions directly into the document, enhancing the fluidity of text revision. Research and innovation in the latter kind of interface can help AI-supported writers become more productive as they revise text.
In our design, we adopt an in-place editing interface in a GPT-4 powered research prototype, offering a solution to overcome challenges surrounding the management of multiple text variations in human-AI co-writing tasks. We carefully construct a baseline interface representing current workflows, providing fresh empirical insights based on our interviews with writers. These insights help us understand user perceptions of the revision process and explore how differences between in-place editing and chat-based AI writing companions impact their workflow.
Designing and Evaluating ABScribe
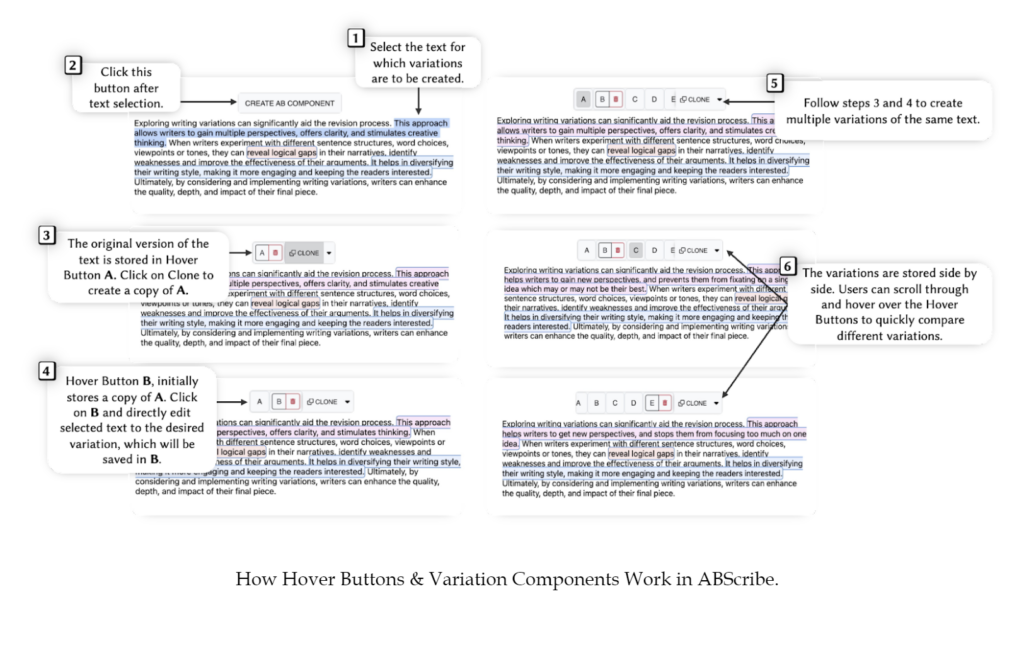
ABScribe is built on four design requirements that support AI-assisted revision: minimizing task workload, visually organizing text variations, allowing context-sensitive comparison and revision, and enabling revision-centric, reusable AI prompts. We designed five interface elements to embody these requirements, allowing writers to seamlessly explore multiple writing variations: (i) Variation Components that store multiple human and AI-generated variations within flexible text segments in a non-linear manner, without overwriting text; (ii) Hover Buttons that reveal corresponding versions inside a Variation Component when users hover their mouse over them, allowing for rapid comparisons without breaking text flow; (iii) the Variation Accordion that organizes all variations in a navigable format; (iv) AI Buttons that automatically encapsulates LLM instructions into reusable buttons that can be applied across different Variation Components; and (v) AI Insert that allows writers to insert LLM-generated text directly into the document.

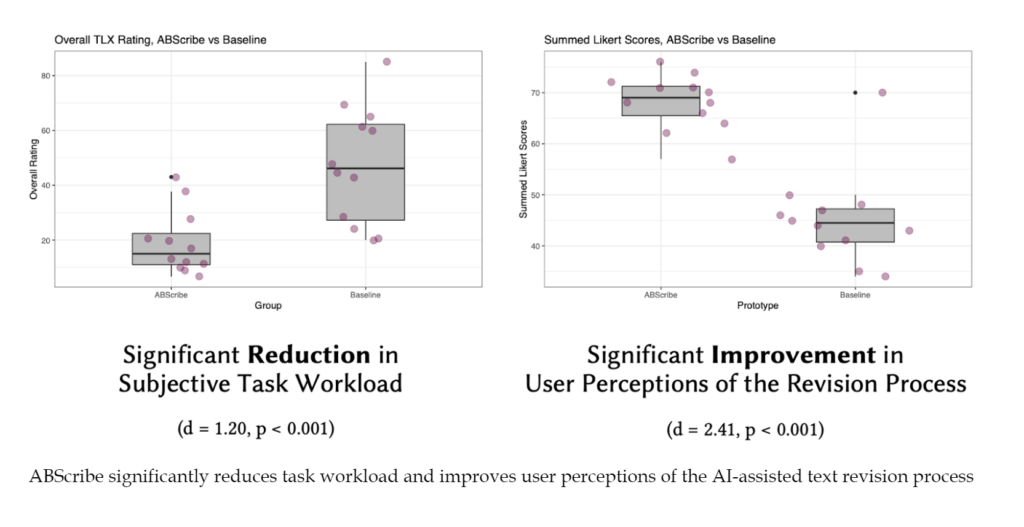
To validate our design, we conducted a controlled evaluation study and interviews with 12 writers comparing ABScribe with a widely-used baseline workflow consisting of an AI-integrated rich text editor based on GPT-4 with a chat-based AI assistant. Our findings demonstrate that ABScribe significantly reduces subjective task workload (d = 1.20, p<0.001) and enhances user perceptions of the revision process (d = 2.41, p<0.001) compared to the baseline.
Between the lines
The text-editing interfaces in use today were designed before computers learned to write like humans. As such, researchers must critically reassess these interfaces as we integrate AI into our daily writing practices. As we transition from using computers as mere tools to embracing them as partners in creativity, the imperative is clear: We must develop the next generation of interfaces, such as ABScribe, to ensure they augment rather than usurp human creativity. Yet, questions linger: How will editing interfaces evolve to balance AI’s sophistication with the user’s need for simplicity? Can we maintain the authenticity of human expression amidst AI’s input? And what new forms of writing will emerge from this symbiosis?
